Tail Angle Preprocessing#
The following notebook illustrate the TailPreprocessing class how to run the different preprocessing steps.
Several preprocessing steps are used for the tail angle:
Interpolating missing values
PCA denoising of posture using ‘eigen-fish’
Savgol filter for time series smoothing
Baseline correction
The tail vigor is also computed and will be useful for detecting tail bouts
Loading dependencies
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from megabouts.tracking_data import TrackingConfig, FullTrackingData, load_example_data
from megabouts.config import TailPreprocessingConfig
from megabouts.preprocessing import TailPreprocessing
Loading Data#
TrackingConfig and TrackingData similar to tutorial_Loading_Data, here we use the dataset from the poorly trained SLEAP model to underlie the effect of smoothing.
# Load data and set tracking configuration
df_recording, fps, mm_per_unit = load_example_data("SLEAP_fulltracking")
tracking_cfg = TrackingConfig(fps=fps, tracking="full_tracking")
# List of keypoints
keypoints = ["left_eye", "right_eye", "tail0", "tail1", "tail2", "tail3", "tail4"]
# Place NaN where the score is below a threshold
thresh_score = 0.0
for kps in keypoints:
score_below_thresh = df_recording["instance.score"] < thresh_score
df_recording.loc[
score_below_thresh | (df_recording[f"{kps}.score"] < thresh_score),
[f"{kps}.x", f"{kps}.y"],
] = np.nan
# Compute head and tail coordinates and convert to mm
head_x = ((df_recording["left_eye.x"] + df_recording["right_eye.x"]) / 2) * mm_per_unit
head_y = ((df_recording["left_eye.y"] + df_recording["right_eye.y"]) / 2) * mm_per_unit
tail_x = df_recording[[f"tail{i}.x" for i in range(5)]].values * mm_per_unit
tail_y = df_recording[[f"tail{i}.y" for i in range(5)]].values * mm_per_unit
# Create FullTrackingData object
tracking_data = FullTrackingData.from_keypoints(
head_x=head_x.values, head_y=head_y.values, tail_x=tail_x, tail_y=tail_y
)
Run Preprocessing#
Define preprocessing config using default:
tail_preprocessing_cfg = TailPreprocessingConfig(fps=tracking_cfg.fps)
print(tail_preprocessing_cfg)
TailPreprocessingConfig(fps=350, limit_na_ms=100, num_pcs=4, savgol_window_ms=15, baseline_method='median', baseline_params={'fps': 350, 'half_window': 175}, tail_speed_filter_ms=100, tail_speed_boxcar_filter_ms=14)
Alternatively the tail preprocessing parameters can be set to custom values using:
tail_preprocessing_cfg = TailPreprocessingConfig(
fps=tracking_cfg.fps,
num_pcs=3,
savgol_window_ms=30,
tail_speed_filter_ms=100,
tail_speed_boxcar_filter_ms=14,
)
Here we change the median filter for computing the tail baseline to 200 frame width:
tail_preprocessing_cfg.baseline_params["half_window"] = 100
Let’s run the preprocessing pipeline:
tail_df_input = tracking_data.tail_df
tail = TailPreprocessing(tail_preprocessing_cfg).preprocess_tail_df(tail_df_input)
tail.df contains information about the raw angle, the baseline, the smooth angle as well as the vigor of the tail oscillations:
tail.df.head(5)
| angle | ... | angle_smooth | no_tracking | vigor | |||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| segments | ... | segments | |||||||||||||||||||
| 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | ... | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | |||
| 0 | 0.122614 | -0.015221 | -0.098553 | -0.126124 | -0.098301 | -0.015937 | 0.062022 | 0.057392 | -0.035583 | -0.215341 | ... | -0.100224 | -0.096774 | -0.067329 | -0.018151 | 0.056155 | 0.058781 | -0.090561 | -0.172721 | False | NaN |
| 1 | 0.122639 | -0.015076 | -0.098353 | -0.125934 | -0.098185 | -0.015953 | 0.061969 | 0.057438 | -0.035308 | -0.214723 | ... | -0.086259 | -0.081402 | -0.051451 | -0.002093 | 0.069939 | 0.071179 | -0.076765 | -0.157507 | False | NaN |
| 2 | 0.122712 | -0.015160 | -0.098521 | -0.126112 | -0.098298 | -0.015927 | 0.062090 | 0.057466 | -0.035575 | -0.215469 | ... | -0.077366 | -0.071614 | -0.041347 | 0.008123 | 0.078698 | 0.079057 | -0.067974 | -0.147809 | False | NaN |
| 3 | 0.182927 | 0.045016 | -0.038378 | -0.065993 | -0.038198 | 0.044170 | 0.122267 | 0.117708 | 0.024690 | -0.155223 | ... | -0.073543 | -0.067412 | -0.037017 | 0.012494 | 0.082430 | 0.082415 | -0.064188 | -0.143629 | False | NaN |
| 4 | 0.182883 | 0.045139 | -0.038150 | -0.065731 | -0.037968 | 0.044304 | 0.122333 | 0.117786 | 0.024859 | -0.154890 | ... | -0.074792 | -0.068794 | -0.038462 | 0.011022 | 0.081137 | 0.081254 | -0.065407 | -0.144965 | False | NaN |
5 rows × 32 columns
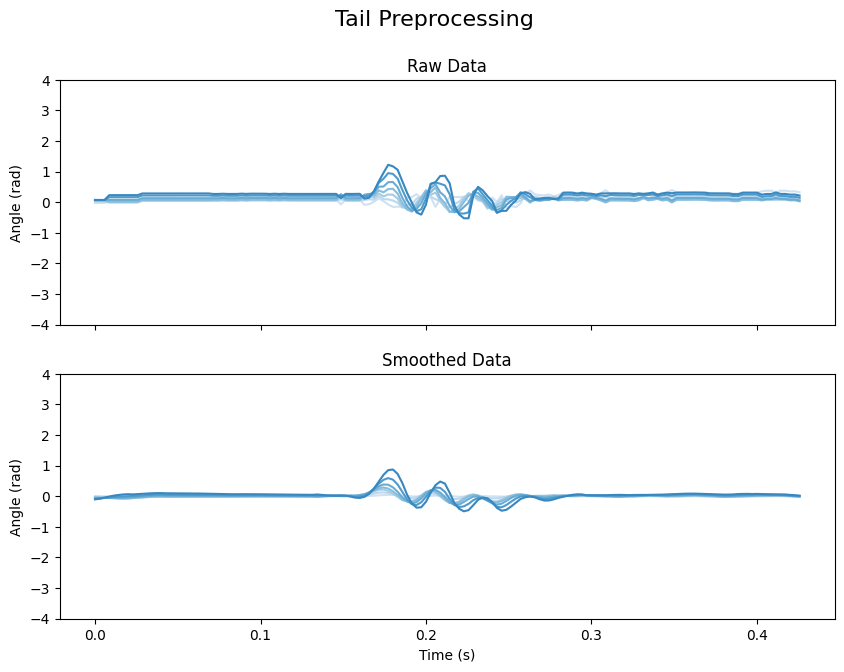
We can visualize the result of preprocessing:
Show code cell source
from cycler import cycler
blue_cycler = cycler(color=plt.cm.Blues(np.linspace(0.2, 0.9, 10)))
t = np.arange(tracking_data.T) / tracking_cfg.fps
IdSt = 140612 # np.random.randint(tracking_data.T)
Duration = 150
t_win = t[IdSt : IdSt + Duration] - t[IdSt]
# Prepare the data, titles, and subtitles
angle_data = [tail.angle, tail.angle_smooth]
subtitles = ["Raw Data", "Smoothed Data"]
# Create subplots
fig, ax = plt.subplots(2, 1, figsize=(10, 7), sharex=True)
# Set a main title for the figure
fig.suptitle("Tail Preprocessing", fontsize=16)
# Loop over the axes, data, and subtitles
for axis, data, subtitle in zip(ax, angle_data, subtitles):
axis.set_prop_cycle(blue_cycler)
axis.plot(t_win, data[IdSt : IdSt + Duration, :7])
axis.set(ylabel="Angle (rad)", ylim=(-4, 4))
axis.set_title(subtitle, fontsize=12)
# Set x-label for the last subplot
ax[-1].set_xlabel("Time (s)")
plt.show()
📝 Note
Smoothing the tail tracking data is optional for classifying tail bouts. The transformer model was trained on raw tracking data, so it can handle unsmoothed input just as well.